参考文章:IntersectionObserver API 使用教程
Intersection Observer
【译】使用 Intersection Observer 实现图片延迟加载
intersectionObserver解决什么问题?
intersectionObserver解决目标元素与视口产生一个交叉区,所以这个 API 叫做”交叉观察器”,
比如在web网页开发中,常常需要了解某个元素是否进入了”视口”(viewport),即用户能不能看到它。
传统的实现方法是,监听到scroll事件后,调用目标元素(绿色方块)的getBoundingClientRect()方法,得到它对应于视口左上角的坐标,再判断是否在视口之内。这种方法的缺点是,由于scroll事件密集发生,计算量很大,容易造成性能问题。
目前有一个新的 IntersectionObserver API,可以自动”观察”元素是否可见,Chrome 51+ 已经支持。由于可见(visible)的本质是,目标元素与视口产生一个交叉区,所以这个 API 叫做”交叉观察器”。
IntersectionObserver API 是异步的,不随着目标元素的滚动同步触发。规格写明,
IntersectionObserver的实现,应该采用requestIdleCallback(),即只有线程空闲下来,才会执行观察器。这意味着,这个观察器的优先级非常低,只在其他任务执行完,浏览器有了空闲才会执行。
IntersectionObserverEntry 对象
IntersectionObserverEntry对象提供目标元素的信息,一共有六个属性。
{
time: 3893.92,
rootBounds: ClientRect {
bottom: 920,
height: 1024,
left: 0,
right: 1024,
top: 0,
width: 920 },
boundingClientRect: ClientRect { // ...
},
intersectionRect: ClientRect { // ...
},
intersectionRatio: 0.54,
target: element
}
每个属性的含义如下。
time:可见性发生变化的时间,是一个高精度时间戳,单位为毫秒target:被观察的目标元素,是一个 DOM 节点对象rootBounds:根元素的矩形区域的信息,getBoundingClientRect()方法的返回值,如果没有根元素(即直接相对于视口滚动),则返回nullboundingClientRect:目标元素的矩形区域的信息intersectionRect:目标元素与视口(或根元素)的交叉区域的信息intersectionRatio:目标元素的可见比例,即intersectionRect占boundingClientRect的比例,完全可见时为1,完全不可见时小于等于0
现在我们已经创建了一个 Intersection Observer 并且正在观察页面上的图片,我们现在来了解 intersection 事件,它将在元素进入视区时触发。
浏览器支持
此时此刻,你也许想知道关于这项特性的浏览器支持情况。Intersection Observer 现在已被 Edge、Firefox、Chrome 和 Opera 支持,这是一个好消息。
然而,为了确保我们的代码不会在不支持它的浏览器中造成破坏,我们可以使用特性检测来确定我们应该如何来加载图片。让我们看看下面的代码。
// If we don't have support for intersection observer, load the images immediately
if (!('IntersectionObserver' in window)) {
Array.from(images).forEach(image => preloadImage(image));
} else {
// It is supported, load the images
observer = new IntersectionObserver(onIntersection, config);
images.forEach(image => {
observer.observe(image);
});
}
view raw
Vue:
<template>
<img :src="lazysrc" />
</template>
<script>
import Bus from '../bus';
import nonepng from '../../assets/img/none.png';
export default {
name: 'lazyimg',
data: function() {
return {
isShow: false,
lazysrc: nonepng
}
},
mounted() {
if(!this.needlazy) {
this.lazysrc = this.src;
} else {
if(!('IntersectionObserver' in window)) {
//TODO
} else {
var io = new IntersectionObserver(
entries => {
entries.forEach(i => {
if(i.intersectionRatio >= 0.25) { //可见元素占视窗的25%触发
i.target.setAttribute("src", this.src)
}
});
}, {
threshold: [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1],
}
);
io.observe(this.$el);
}
}
},
props: {
needlazy: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
src: {
type: String,
default: '',
},
}
};
</script>
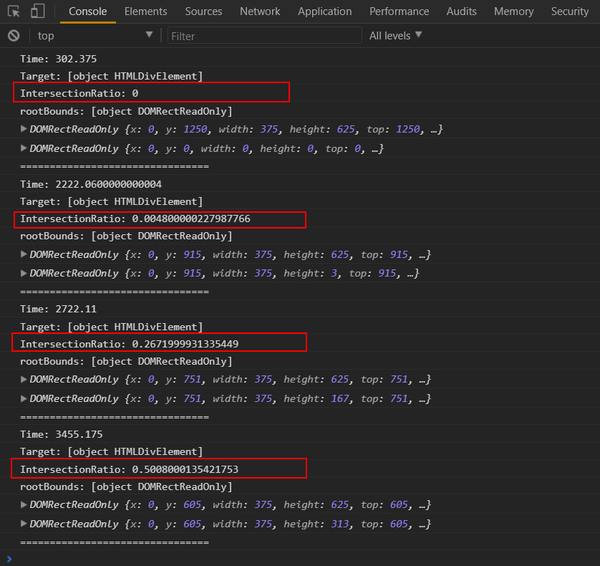
通常都是通过判断intersectionRatio来做某些事,比如当intersectionRatio大于多少的时候做什么事,加载图片等!


灰色的水平方框代表视口,深红色的区域代表四个被观察的目标元素。它们各自的intersectionRatio图中都已经注明。
DEMO: 延迟加载(Lazyload)三种实现方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width">
<title> </title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
outline: none;
}
body {}
#main {
margin: 0 auto;
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
overflow: scroll;
}
#con {
width: 1200px;
height: 300px;
}
.cc {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
float: left;
background-size: cover;
}
#a {
background-color: red;
}
#b {
background-color: black;
}
#c {
background-color: blue;
}
#d {
background-color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main">
<div id="con">
<div id="a" class="cc"></div>
<div id="b" class="cc"></div>
<div id="c" class="cc"></div>
<div id="d" class="cc"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var io = new IntersectionObserver(
entries => {
console.log('********************************');
console.log(entries);
console.log('********************************');
entries.forEach(i => {
console.log('================================');
console.log('Time: ' + i.time);
console.log('Target: ' + i.target.nodeName);
console.log('IntersectionRatio: ' + i.intersectionRatio);
console.log('rootBounds: ' + i.rootBounds);
console.log(i.boundingClientRect);
console.log(i.intersectionRect);
console.log('================================');
if(i.intersectionRatio >= 0.25) { //可见元素占视窗的25%触发
console.log('^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^');
i.target.style.backgroundImage = "url(" + 'http://pic35.photophoto.cn/20150528/0020032932102307_b.jpg' + ")"
}
});
}, {
/* Using default options. Details below */
threshold: [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1], //会执行5次
}
);
// Start observing an element
io.observe(document.querySelector('#d'));
io.observe(document.querySelector('#c'));
</script>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Lazyload 3</title>
<style>
img {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 50px;
width: 800px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/1.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/2.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/3.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/4.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/5.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/6.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/7.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/8.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/9.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/10.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/11.png">
<img src="images/loading.gif" data-src="images/12.png">
<script>
function query(selector) {
return Array.from(document.querySelectorAll(selector));
}
var io = new IntersectionObserver(function(items) {
items.forEach(function(item) {
var target = item.target;
if(target.getAttribute('src') == 'images/loading.gif') {
target.src = target.getAttribute('data-src');
}
})
});
query('img').forEach(function(item) {
io.observe(item);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
- IntersectionObserver 传入一个回调函数,当其观察到元素集合出现时候,则会执行该函数。
- io.observe 即要观察的元素,要一个个添加才可以。
- io 管理的是一个数组,当元素出现或消失的时候,数组添加或删除该元素,并且执行该回调函数。
一、API
它的用法非常简单。
var io = new IntersectionObserver(callback, option);
上面代码中,IntersectionObserver是浏览器原生提供的构造函数,接受两个参数:callback是可见性变化时的回调函数,option是配置对象(该参数可选)。
构造函数的返回值是一个观察器实例。实例的observe方法可以指定观察哪个 DOM 节点。
// 开始观察
io.observe(document.getElementById('example'));
// 停止观察
io.unobserve(element);
// 关闭观察器
io.disconnect();
上面代码中,observe的参数是一个 DOM 节点对象。如果要观察多个节点,就要多次调用这个方法。
io.observe(elementA);
io.observe(elementB);
二、callback 参数
目标元素的可见性变化时,就会调用观察器的回调函数callback。
callback一般会触发两次。一次是目标元素刚刚进入视口(开始可见),另一次是完全离开视口(开始不可见)。
var io = new IntersectionObserver(
entries => {
console.log(entries); }
);
上面代码中,回调函数采用的是箭头函数的写法。callback函数的参数(entries)是一个数组,每个成员都是一个[IntersectionObserverEntry](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserverEntry)对象。举例来说,如果同时有两个被观察的对象的可见性发生变化,entries数组就会有两个成员。
三、Option 对象
IntersectionObserver构造函数的第二个参数是一个配置对象。它可以设置以下属性。
[IntersectionObserver.root](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/root) 只读所监听对象的具体祖先元素([element](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Element))。如果未传入任何值或值为null,则默认使用viewport。
[IntersectionObserver.rootMargin](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/rootMargin) 只读计算交叉时添加到根(root)边界盒bounding box的矩形偏移量, 可以有效的缩小或扩大根的判定范围从而满足计算需要。此属性返回的值可能与调用构造函数时指定的值不同,因此可能需要更改该值,以匹配内部要求。所有的偏移量均可用像素(pixel)(px)或百分比(percentage)(%)来表达, 默认值为”0px 0px 0px 0px”。
[IntersectionObserver.thresholds](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/thresholds) 只读一个包含阈值的list, 升序排列, list中的每个阈值都是监听对象的交叉区域与边界区域的比率。当监听对象的任何阈值被越过时,都会生成一个通知(Notification)。如果构造器未传入值, 则默认值为0.
threshold 属性
threshold属性决定了什么时候触发回调函数。它是一个数组,每个成员都是一个门槛值,默认为[0],即交叉比例(intersectionRatio)达到0时触发回调函数。
new IntersectionObserver(
entries => {/* ... */}, {
threshold: [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1] } );
用户可以自定义这个数组。比如,[0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1]就表示当目标元素 0%、25%、50%、75%、100% 可见时,会触发回调函数。
root 属性,rootMargin 属性
很多时候,目标元素不仅会随着窗口滚动,还会在容器里面滚动(比如在iframe窗口里滚动)。容器内滚动也会影响目标元素的可见性,参见本文开始时的那张示意图。
IntersectionObserver API 支持容器内滚动。root属性指定目标元素所在的容器节点(即根元素)。注意,容器元素必须是目标元素的祖先节点。
var opts = {
root: document.querySelector('.container'),
rootMargin: "500px 0px"
};
var observer = new IntersectionObserver(
callback,
opts
);
上面代码中,除了root属性,还有[rootMargin](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//wicg.github.io/IntersectionObserver/%23dom-intersectionobserverinit-rootmargin)属性。后者定义根元素的margin,用来扩展或缩小rootBounds这个矩形的大小,从而影响intersectionRect交叉区域的大小。它使用CSS的定义方法,比如10px 20px 30px 40px,表示 top、right、bottom 和 left 四个方向的值。
//离视窗还有top=500px 或者 bottom=500 触发加载
rootMargin = `500px 0px`
//离视窗还有top=-500px 或者 bottom=-500 触发加载 (惰性加载)
rootMargin = `-500px 0px`
这样设置以后,不管是窗口滚动或者容器内滚动,只要目标元素可见性变化,都会触发观察器。
四、方法
[IntersectionObserver.disconnect](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/disconnect)使IntersectionObserver对象停止监听工作。
[IntersectionObserver.observe](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/observe)使IntersectionObserver开始监听一个目标元素。
[IntersectionObserver.takeRecords](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/takeRecords)为所有监听目标返回一个[IntersectionObserverEntry](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserverEntry)对象数组并且停止监听这些目标。
[IntersectionObserver.unobserve](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/IntersectionObserver/unobserve)使IntersectionObserver停止监听特定目标元素。
五、Vue(xunleif2e/vue-lazy-component)
核心 VueLazyComponent.vue
<template>
<transition-group :tag="tagName" name="lazy-component" style="position: relative;"
@before-enter="(el) => $emit('before-enter', el)"
@before-leave="(el) => $emit('before-leave', el)"
@after-enter="(el) => $emit('after-enter', el)"
@after-leave="(el) => $emit('after-leave', el)"
>
<div v-if="isInit" key="component">
<slot :loading="loading"></slot>
</div>
<div v-else-if="$slots.skeleton" key="skeleton">
<slot name="skeleton"></slot>
</div>
<div v-else key="loading">
</div>
</transition-group>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'VueLazyComponent',
props: {
timeout: {
type: Number
},
tagName: {
type: String,
default: 'div'
},
viewport: {
type: typeof window !== 'undefined' ? window.HTMLElement : Object,
default: () => null
},
threshold: {
type: String,
default: '0px'
},
direction: {
type: String,
default: 'vertical'
},
maxWaitingTime: {
type: Number,
default: 50
}
},
data () {
return {
isInit: false,
timer: null,
io: null,
loading: false
}
},
created () {
// 如果指定timeout则无论可见与否都是在timeout之后初始化
if (this.timeout) {
this.timer = setTimeout(() => {
this.init()
}, this.timeout)
}
},
mounted () {
if (!this.timeout) {
// 根据滚动方向来构造视口外边距,用于提前加载
let rootMargin
switch (this.direction) {
case 'vertical':
rootMargin = `${this.threshold} 0px`
break
case 'horizontal':
rootMargin = `0px ${this.threshold}`
break
}
// 观察视口与组件容器的交叉情况
this.io = new window.IntersectionObserver(this.intersectionHandler, {
rootMargin,
root: this.viewport,
threshold: [ 0, Number.MIN_VALUE, 0.01]
})
this.io.observe(this.$el)
}
},
beforeDestroy () {
// 在组件销毁前取消观察
if (this.io) {
this.io.unobserve(this.$el)
}
},
methods: {
// 交叉情况变化处理函数
intersectionHandler (entries) {
if (
// 正在交叉
entries[0].isIntersecting ||
// 交叉率大于0
entries[0].intersectionRatio
) {
this.init()
this.io.unobserve(this.$el)
}
},
// 处理组件和骨架组件的切换
init () {
// 此时说明骨架组件即将被切换
this.$emit('beforeInit')
this.$emit('before-init')
// 此时可以准备加载懒加载组件的资源
this.loading = true
// 由于函数会在主线程中执行,加载懒加载组件非常耗时,容易卡顿
// 所以在requestAnimationFrame回调中延后执行
this.requestAnimationFrame(() => {
this.isInit = true
this.$emit('init')
})
},
requestAnimationFrame (callback) {
// 防止等待太久没有执行回调
// 设置最大等待时间
setTimeout(() => {
if (this.isInit) return
callback()
}, this.maxWaitingTime)
// 兼容不支持requestAnimationFrame 的浏览器
return (window.requestAnimationFrame || ((callback) => setTimeout(callback, 1000 / 60)))(callback)
}
}
}
</script>