call
一句话介绍 call:
call() 方法在使用一个指定的 this 值和若干个指定的参数值的前提下调用某个函数或方法。
举个例子:
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar() {
console.log(this.value);
}
bar.call(foo); // 1
注意两点:
- call 改变了 this 的指向,指向到 foo
- bar 函数执行了
模拟实现第一步
那么我们该怎么模拟实现这两个效果呢?
试想当调用 call 的时候,把 foo 对象改造成如下:
var foo = {
value: 1,
bar: function() {
console.log(this.value)
}
};
foo.bar(); // 1
这个时候 this 就指向了 foo,是不是很简单呢?
但是这样却给 foo 对象本身添加了一个属性,这可不行呐!
不过也不用担心,我们用 delete 再删除它不就好了~
所以我们模拟的步骤可以分为:
- 将函数设为对象的属性
- 执行该函数
- 删除该函数
以上个例子为例,就是:
// 第一步
foo.fn = bar
// 第二步
foo.fn()
// 第三步
delete foo.fn
fn 是对象的属性名,反正最后也要删除它,所以起成什么都无所谓。
根据这个思路,我们可以尝试着去写第一版的 call2 函数:
// 第一版
Function.prototype.call2 = function(context) {
// 首先要获取调用call的函数,用this可以获取
context.fn = this;
context.fn();
delete context.fn;
}
// 测试一下
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar() {
console.log(this.value);
}
bar.call2(foo); // 1
正好可以打印 1 哎!是不是很开心!(~ ̄▽ ̄)~
模拟实现第二步
最一开始也讲了,call 函数还能给定参数执行函数。举个例子:
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar(name, age) {
console.log(name)
console.log(age)
console.log(this.value);
}
bar.call(foo, 'kevin', 18);
// kevin
// 18
// 1
注意:传入的参数并不确定,这可咋办?
不急,我们可以从 Arguments 对象中取值,取出第二个到最后一个参数,然后放到一个数组里。
比如这样:
// 以上个例子为例,此时的arguments为:
// arguments = {
// 0: foo,
// 1: 'kevin',
// 2: 18,
// length: 3
// }
// 因为arguments是类数组对象,所以可以用for循环
var args = [];
for(var i = 1, len = arguments.length; i < len; i++) {
args.push('arguments[' + i + ']');
}
// 执行后 args为 [foo, 'kevin', 18]
不定长的参数问题解决了,我们接着要把这个参数数组放到要执行的函数的参数里面去。
// 将数组里的元素作为多个参数放进函数的形参里
context.fn(args.join(','))
// (O_o)??
// 这个方法肯定是不行的啦!!!
也许有人想到用 ES6 的方法,不过 call 是 ES3 的方法,我们为了模拟实现一个 ES3 的方法,要用到ES6的方法,好像……,嗯,也可以啦。但是我们这次用 eval 方法拼成一个函数,类似于这样:
eval('context.fn(' + args +')')
这里 args 会自动调用 Array.toString() 这个方法。
所以我们的第二版克服了两个大问题,代码如下:
// 第二版
Function.prototype.call2 = function(context) {
context.fn = this;
var args = [];
for(var i = 1, len = arguments.length; i < len; i++) {
args.push('arguments[' + i + ']');
}
eval('context.fn(' + args +')');
delete context.fn;
}
// 测试一下
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar(name, age) {
console.log(name)
console.log(age)
console.log(this.value);
}
bar.call2(foo, 'kevin', 18);
// kevin
// 18
// 1
(๑•̀ㅂ•́) ✧
模拟实现第三步
模拟代码已经完成 80%,还有两个小点要注意:
1.this 参数可以传 null,当为 null 的时候,视为指向 window
举个例子:
var value = 1;
function bar() {
console.log(this.value);
}
bar.call(null); // 1
虽然这个例子本身不使用 call,结果依然一样。
2.函数是可以有返回值的!
举个例子:
var obj = {
value: 1
}
function bar(name, age) {
return {
value: this.value,
name: name,
age: age
}
}
console.log(bar.call(obj, 'kevin', 18));
// Object {
// value: 1,
// name: 'kevin',
// age: 18
// }
不过都很好解决,让我们直接看第三版也就是最后一版的代码:
// 第三版
Function.prototype.call2 = function (context) {
var context = context || window;
context.fn = this;
var args = [];
for(var i = 1, len = arguments.length; i < len; i++) {
args.push('arguments[' + i + ']');
}
var result = eval('context.fn(' + args +')');
delete context.fn
return result;
}
// 测试一下
var value = 2;
var obj = {
value: 1
}
function bar(name, age) {
console.log(this.value);
return {
value: this.value,
name: name,
age: age
}
}
bar.call(null); // 2
console.log(bar.call2(obj, 'kevin', 18));
// 1
// Object {
// value: 1,
// name: 'kevin',
// age: 18
// }
到此,我们完成了 call 的模拟实现,给自己一个赞 b( ̄▽ ̄)d
apply的模拟实现
apply 的实现跟 call 类似,在这里直接给代码,代码来自于知乎 @郑航的实现:
Function.prototype.apply = function (context, arr) {
var context = Object(context) || window;
context.fn = this;
var result;
if (!arr) {
result = context.fn();
}
else {
var args = [];
for (var i = 0, len = arr.length; i < len; i++) {
args.push('arr[' + i + ']');
}
result = eval('context.fn(' + args + ')')
}
delete context.fn
return result;
}


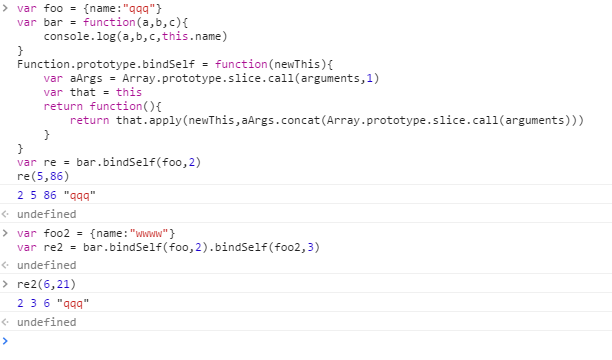
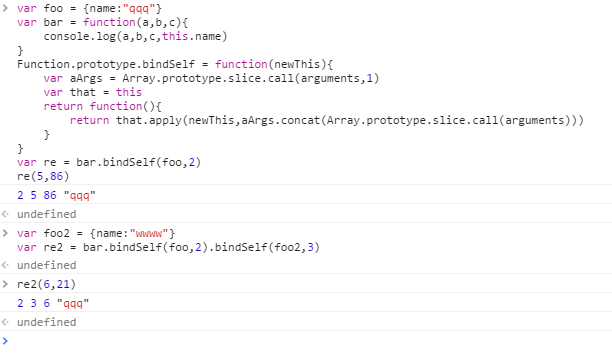
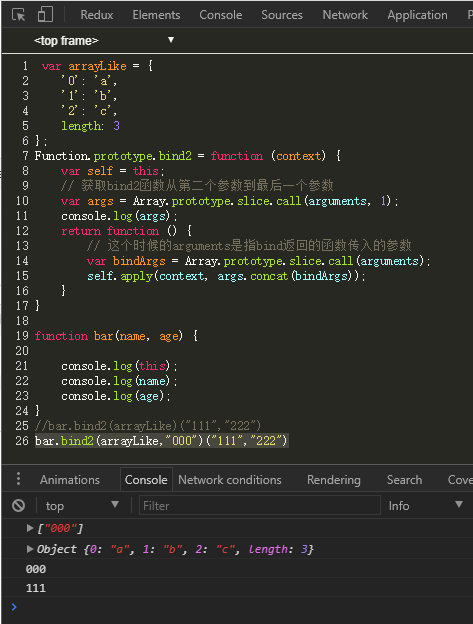
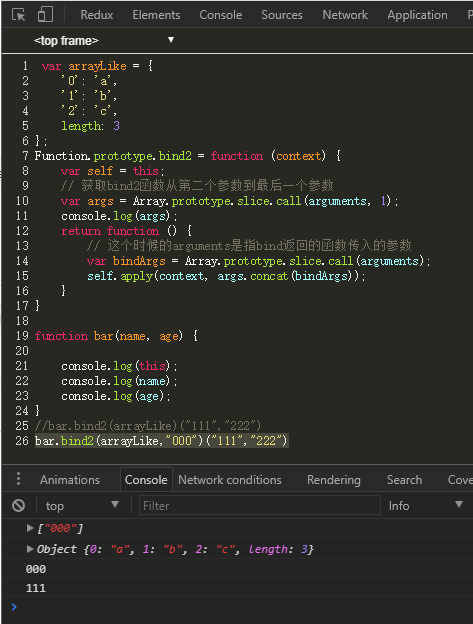

类数组转对象
在上面的例子中已经提到了一种类数组转数组的方法,再补充三个:
var arrayLike = {0: 'name', 1: 'age', 2: 'sex', length: 3 }
// 1. slice
Array.prototype.slice.call(arrayLike); // ["name", "age", "sex"]
// 2. splice
Array.prototype.splice.call(arrayLike, 0); // ["name", "age", "sex"]
// 3. ES6 Array.from
Array.from(arrayLike); // ["name", "age", "sex"]
// 4. apply
Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arrayLike)
要说到类数组对象,Arguments 对象就是一个类数组对象。
在客户端 JavaScript 中,一些 DOM 方法(document.getElementsByTagName()等)也返回类数组对象。
传递参数
将参数从一个函数传递到另一个函数
// 使用 apply 将 foo 的参数传递给 bar
function foo() {
bar.apply(this, arguments);
}
function bar(a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c);
}
foo(1, 2, 3)
强大的ES6
使用ES6的 ... 运算符,我们可以轻松转成数组。
function func(...arguments) {
console.log(arguments); // [1, 2, 3]
}
func(1, 2, 3);
bind
一句话介绍 bind:
bind() 方法会创建一个新函数。当这个新函数被调用时,bind() 的第一个参数将作为它运行时的 this,之后的一序列参数将会在传递的实参前传入作为它的参数。(来自于 MDN )
由此我们可以首先得出 bind 函数的两个特点:
- 返回一个函数
- 可以传入参数
返回函数的模拟实现
从第一个特点开始,我们举个例子:
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar() {
console.log(this.value);
}
// 返回了一个函数
var bindFoo = bar.bind(foo);
bindFoo(); // 1
关于指定 this 的指向,我们可以使用 call 或者 apply 实现,关于 call 和 apply 的模拟实现,可以查看《JavaScript深入之call和apply的模拟实现》。我们来写第一版的代码:
// 第一版
Function.prototype.bind2 = function (context) {
var self = this;
return function () {
self.apply(context);
}
}
传参的模拟实现
接下来看第二点,可以传入参数。这个就有点让人费解了,我在 bind 的时候,是否可以传参呢?我在执行 bind 返回的函数的时候,可不可以传参呢?让我们看个例子:
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar(name, age) {
console.log(this.value);
console.log(name);
console.log(age);
}
var bindFoo = bar.bind(foo, 'daisy');
bindFoo('18');
// 1
// daisy
// 18
函数需要传 name 和 age 两个参数,竟然还可以在 bind 的时候,只传一个 name,在执行返回的函数的时候,再传另一个参数 age!
这可咋办?不急,我们用 arguments 进行处理:
// 第二版
Function.prototype.bind2 = function (context) {
var self = this;
// 获取bind2函数从第二个参数到最后一个参数
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
return function () {
// 这个时候的arguments是指bind返回的函数传入的参数
var bindArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
self.apply(context, args.concat(bindArgs));
}
}
构造函数效果的模拟实现
完成了这两点,最难的部分到啦!因为 bind 还有一个特点,就是
一个绑定函数也能使用new操作符创建对象:这种行为就像把原函数当成构造器。提供的 this 值被忽略,同时调用时的参数被提供给模拟函数。
也就是说当 bind 返回的函数作为构造函数的时候,bind 时指定的 this 值会失效,但传入的参数依然生效。举个例子:
var value = 2;
var foo = {
value: 1
};
function bar(name, age) {
this.habit = 'shopping';
console.log(this.value);
console.log(name);
console.log(age);
}
bar.prototype.friend = 'kevin';
var bindFoo = bar.bind(foo, 'daisy');
var obj = new bindFoo('18');
// undefined
// daisy
// 18
console.log(obj.habit);
console.log(obj.friend);
// shopping
// kevin
注意:尽管在全局和 foo 中都声明了 value 值,最后依然返回了 undefind,说明绑定的 this 失效了,如果大家了解 new 的模拟实现,就会知道这个时候的 this 已经指向了 obj。
(哈哈,我这是为我的下一篇文章《JavaScript深入系列之new的模拟实现》打广告)。
所以我们可以通过修改返回的函数的原型来实现,让我们写一下:
// 第三版
Function.prototype.bind2 = function (context) {
var self = this;
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
var fBound = function () {
var bindArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
// 当作为构造函数时,this 指向实例,此时结果为 true,将绑定函数的 this 指向该实例,可以让实例获得来自绑定函数的值
// 以上面的是 demo 为例,如果改成 `this instanceof fBound ? null : context`,实例只是一个空对象,将 null 改成 this ,实例会具有 habit 属性
// 当作为普通函数时,this 指向 window,此时结果为 false,将绑定函数的 this 指向 context
self.apply(this instanceof fBound ? this : context, args.concat(bindArgs));
}
// 修改返回函数的 prototype 为绑定函数的 prototype,实例就可以继承绑定函数的原型中的值
fBound.prototype = this.prototype;
return fBound;
}
如果对原型链稍有困惑,可以查看《JavaScript深入之从原型到原型链》。
构造函数效果的优化实现
但是在这个写法中,我们直接将 fBound.prototype = this.prototype,我们直接修改 fBound.prototype 的时候,也会直接修改绑定函数的 prototype。这个时候,我们可以通过一个空函数来进行中转:
// 第四版
Function.prototype.bind2 = function (context) {
var self = this;
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
var fNOP = function () {};
var fBound = function () {
var bindArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
self.apply(this instanceof fNOP ? this : context, args.concat(bindArgs));
}
fNOP.prototype = this.prototype;
fBound.prototype = new fNOP();
return fBound;
}
到此为止,大的问题都已经解决,给自己一个赞!o( ̄▽ ̄)d
三个小问题
接下来处理些小问题:
1.apply 这段代码跟 MDN 上的稍有不同
在 MDN 中文版讲 bind 的模拟实现时,apply 这里的代码是:
self.apply(this instanceof self ? this : context || this, args.concat(bindArgs))
多了一个关于 context 是否存在的判断,然而这个是错误的!
举个例子:
var value = 2;
var foo = {
value: 1,
bar: bar.bind(null)
};
function bar() {
console.log(this.value);
}
foo.bar() // 2
以上代码正常情况下会打印 2,如果换成了 context || this,这段代码就会打印 1!
所以这里不应该进行 context 的判断,大家查看 MDN 同样内容的英文版,就不存在这个判断!
2.调用 bind 的不是函数咋办?
不行,我们要报错!
if (typeof this !== "function") {
throw new Error("Function.prototype.bind - what is trying to be bound is not callable");
}
3.我要在线上用
那别忘了做个兼容:
Function.prototype.bind = Function.prototype.bind || function () {
……
};
当然最好是用 es5-shim 啦。
最终代码
所以最最后的代码就是:
Function.prototype.bind2 = function (context) {
if (typeof this !== "function") {
throw new Error("Function.prototype.bind - what is trying to be bound is not callable");
}
var self = this;
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
var fNOP = function () {};
var fBound = function () {
var bindArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
self.apply(this instanceof fNOP ? this : context, args.concat(bindArgs));
}
fNOP.prototype = this.prototype;
fBound.prototype = new fNOP();
return fBound;
}